Author information
Cristina-Sorina Catana1, Diana Gulei2, Ioana Berindan-Neagoe2, 3, 4*
Download
1Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, ”Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
2Research Center for Advanced Medicine, Medfuture, ”Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
3Research Center for Functional Genomics Biomedicine and Translational Medicine, ”Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
4Department of Functional Genomics, Proteomics and Experimental Pathology,
e Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. Ion Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
2Research Center for Advanced Medicine, Medfuture, ”Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
3Research Center for Functional Genomics Biomedicine and Translational Medicine, ”Iuliu Hațieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
4Department of Functional Genomics, Proteomics and Experimental Pathology,
e Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. Ion Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Abstract
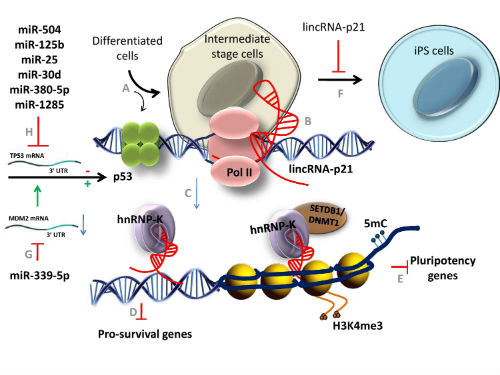
P53 classifies as one of the main tumor suppressor gene and the identification of its direct transcriptional targets such as certain non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) is important for understanding the development and progression of cancer. Multiple ncRNAs are targeting p53 and are involved in many cellular processes such as cell cycle arrest, metabolism, apoptosis, autophagy and feedback mechanisms. Also, various ncRNAs were found to modulate p53-dependent gene regulation. These include microRNAs such as miR-660, miR-486, miR-34 and lncRNAs such as nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1), which contribute to the tumor-suppressor function of the p53 protein. Long intergenic non-coding RNA, LincRNA-p21, has been proclaimed to promote apoptosis while other p53-regulated lncRNAs including PANDA and Pint antagonize p53 activity by limiting the activation of proapoptotic genes. Taking into account the activity of the proapoptotic transcription factor p53, new conclusions point to a new concept of cellular quality control since ncRNAs-based deregulation in cancer functions in the absence of p53 coding sequence mutations.
(Received 26 March, 2017; accepted 8 May, 2017)
Keywords
long non-coding RNAs; p53; apoptosis; lincRNA-p21